Before we dive into a detailed automated testing tools comparison, let’s establish a critical fact: shifting from manual to automated testing isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic necessity for survival in a market that demands speed and flawless user experiences. Companies leveraging automation see a 40% reduction in testing costs and a 90% improvement in defect detection. This guide provides the data-driven insights you need to make the right choice.
Why Automated Testing Is a Strategic Imperative

In today’s development landscape, manual testing is a bottleneck that actively hinders growth. The global automation testing market was valued at $20.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to explode to $52.4 billion by 2028. This explosive growth isn’t arbitrary; it’s a direct response to the pressures of Agile and DevOps methodologies, which thrive on rapid, continuous feedback loops that manual processes simply cannot sustain.
The core reason companies embrace automation isn’t just to find bugs faster—it’s to fundamentally reshape their software delivery lifecycle.
The Business Case for Automation
Viewing test automation as a mere technical task is a critical business error. It’s a strategic investment with a direct, measurable impact on your bottom line, product quality, and competitive standing. The value is clear and quantifiable:
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: Automation enables you to execute thousands of complex test cases in minutes, not days. This empowers teams to release new features and critical updates with a velocity that manual testing makes impossible.
- Enhanced Quality and Reliability: Automated tests act as a regression safety net, catching bugs early in the development cycle. This prevents defects from reaching users, protecting brand reputation and user trust.
- Increased Team Productivity: Automating repetitive, mundane validation tasks frees up skilled QA engineers and developers to focus on high-value activities like complex problem-solving, exploratory testing, and innovation.
The true power of automation lies in its consistency. An automated test script executes precisely the same way every time, eliminating the human error, fatigue, and variability inherent in manual testing.
More Than Just Finding Bugs
To think of these tools as simple bug-finders is a massive understatement. A robust automated testing suite becomes a living, executable specification of your application’s intended behavior. Each test case serves as a guarantee, programmatically confirming that features perform as expected, release after release. This builds an essential safety net, giving developers the confidence to refactor code and innovate without fear of breaking existing functionality.
The contrast with manual testing is stark.
| Manual Testing Drawbacks | Automated Testing Advantages |
|---|---|
| Prone to human error and inconsistency. | Provides repeatable and reliable results. |
| A slow, resource-draining process. | Executes tests rapidly, 24/7, without getting tired. |
| Limited scope for complex, data-heavy scenarios. | Easily handles large-scale regression suites and complex user flows. |
| A poor fit for fast-paced CI/CD pipelines. | Integrates seamlessly into modern DevOps workflows. |
Ultimately, investing in the right tools isn’t just a technical decision. It’s a foundational business choice that unlocks efficiency, guarantees quality, and provides a significant competitive advantage.
Key Criteria for Your Testing Tool Comparison
Starting an automated testing tools comparison without clear evaluation criteria is a recipe for failure. You risk being swayed by flashy features while ignoring the factors that truly determine success: how the tool integrates with your team, technology, and processes.
A common pitfall is focusing solely on a tool’s capabilities instead of asking, “How does this solve our specific problems?” The right tool should feel like a natural extension of your development cycle, not an additional layer of complexity. To avoid this, use a structured evaluation framework.
Core Evaluation Criteria for Automated Testing Tools
| Criterion | What to Look For | Why It Matters for Your Team |
|---|---|---|
| Platform Compatibility | Support for web, mobile (native/web), and APIs. | You need a tool that covers your entire tech stack. Using one tool is far more efficient than juggling several. |
| Team Skill Level | Options for coded, low-code, or no-code test creation. | The tool must match your team’s existing skills. A mismatch leads to a steep learning curve and slow adoption. |
| CI/CD Integration | Seamless plugins for Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, etc. | Automation is pointless if it doesn’t fit into your pipeline. Smooth integration is essential for continuous testing. |
| Reporting & Analytics | Clear dashboards, historical data, and actionable failure analysis. | Good reports help you find and fix bugs faster. Poor reporting just creates more noise. |
| Cost & Scalability | Transparent pricing, concurrent session limits, and total cost of ownership. | The price tag isn’t just the license fee. Consider maintenance, training, and infrastructure costs as you grow. |
Making the right choice comes down to honestly assessing your needs against what each tool offers. The rest of this guide will walk you through how the leading tools stack up against these very criteria.
Technical and Platform Compatibility
Your first filter must be technical feasibility. A tool’s features are irrelevant if it cannot test your application’s technology stack. Your evaluation must begin by answering these fundamental questions:
- Platform Support: Does the tool handle web, mobile, and APIs? Modern applications often require cross-platform testing, and a unified tool can save significant time and reduce complexity.
- Language & Framework Alignment: Does it support the programming languages your team already uses, like JavaScript, Python, or Java? Forcing developers to learn a new language for testing creates friction and slows down adoption.
- CI/CD Integration: How seamlessly does it integrate with your existing CI/CD pipeline, whether that’s Jenkins , GitHub Actions , or Azure DevOps ? This is non-negotiable for achieving true continuous testing.
One detail people often miss is the difference between emulated mobile testing and true native app testing. Emulators are fine for checking responsive web layouts, but they can’t mimic the hardware interactions or OS-level behavior that only real device testing can catch.
Usability and Team Skill Level
Beyond technical specifications, you must consider the human factor. An infinitely powerful tool is worthless if your team finds it unusable. The required skill set and learning curve will directly impact your team’s productivity and the overall success of your automation initiative.
For instance, a classic framework like Selenium offers unparalleled flexibility but requires developers proficient in coding. In contrast, a low-code platform can empower manual QA engineers and business analysts to contribute to the automation effort, distributing the workload and accelerating test creation.
Consider your team’s current composition and future goals:
- Coding vs. Low-Code: Will only developers write tests, or do you need a solution accessible to non-programmers?
- Onboarding Time: How quickly can a new team member start writing meaningful tests?
- Support Systems: What is your plan for troubleshooting? Open-source tools rely on community forums, which can be excellent but inconsistent. Commercial tools typically offer dedicated support, which can be a lifesaver when facing critical roadblocks.
Ultimately, a smart automated testing tools comparison isn’t about ticking boxes. It’s about finding the optimal balance between a tool’s technical power and its practical usability for the people who will work with it daily.
How Automation Is Changing the Game in Testing

The industry-wide move from manual testing is a direct consequence of the demand for speed and quality. Teams are replacing slow, error-prone manual processes with automation, and the returns are significant. This is more than just running tests faster—it’s about re-architecting the entire software delivery process for efficiency and reliability.
At its core, it’s a matter of scale. A human tester is limited by physical and cognitive endurance. An automated script, however, can execute thousands of checks overnight, delivering consistent, reliable results every time. This is especially true for the repetitive grind of regression testing.
The Numbers Speak for Themselves
By automating these repetitive yet critical checks, you empower your QA engineers to focus on what humans do best: creative exploratory testing and investigating complex user scenarios. The impact on the bottom line is clear and well-documented.
Currently, 46% of software teams have automated at least half of their testing, with a proactive 20% automating 75% or more. The results are compelling, with teams slashing testing time and costs by up to 40%. This shift also gives team productivity a massive lift—up to 80%—and boosts defect detection by as much as 90%. You can dig deeper into these test automation statistics to see the full impact.
The real win with automation isn’t just catching bugs earlier. It’s about stopping them from ever getting to production. When you can instantly catch regressions, you build a safety net that lets developers innovate and move fast without worrying about breaking something.
Where Automation Makes the Biggest Difference
While it’s tempting to automate everything, strategic teams focus on areas with the highest return on investment. Certain types of tests are perfect candidates for automation, where it transitions from a “nice-to-have” to an absolute necessity.
Here are high-impact scenarios where automation provides maximum value:
- Regression Testing: This is the classic use case for a reason. Automation excels at running a vast suite of tests repeatedly to ensure new code hasn’t broken existing functionality. Performing this manually is a time-consuming, expensive, and error-prone task in any modern development cycle.
- Data-Driven Testing: Need to test the same workflow with hundreds of different data inputs? Consider verifying a login form with a long list of valid and invalid credentials. Automation is the only practical way to execute this efficiently and accurately.
- API and Integration Testing: Verifying that different services and microservices communicate correctly is critical. Automated API tests are fast, stable, and can be run early in the development process, providing rapid feedback before a UI even exists.
The Perfect Partner for Agile and DevOps
Agile and DevOps are built on the principle of rapid feedback loops. The objective is to move an idea from concept to production as quickly as possible without compromising quality. Automated testing is the engine that drives these feedback loops.
Without it, Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) are not feasible. A developer commits code, a build is automatically triggered, tests are executed, and the entire team receives immediate feedback. This instant validation is what enables high-performing teams to release software multiple times a day instead of once every few months. A good automated testing tools comparison will highlight platforms that integrate seamlessly into these modern workflows, making them a cornerstone of any successful engineering organization.
A Detailed Look at the Top Automated Testing Tools
Choosing the right tool is arguably the most critical decision in your test automation strategy. To do this effectively, we must cut through marketing claims and analyze how these tools perform in real-world scenarios. This involves examining their core architecture, intended use cases, and the practical trade-offs they present.
We’re going to compare four of the most influential names in the space: Selenium , Cypress , Playwright , and Katalon . Each represents a different philosophy—from pure, code-driven frameworks to comprehensive, all-in-one platforms. Understanding these differences is key to matching a tool to your team’s skills, project requirements, and long-term vision.
This chart provides a high-level overview of how popular tools stack up on key metrics like speed, cost, and community size.
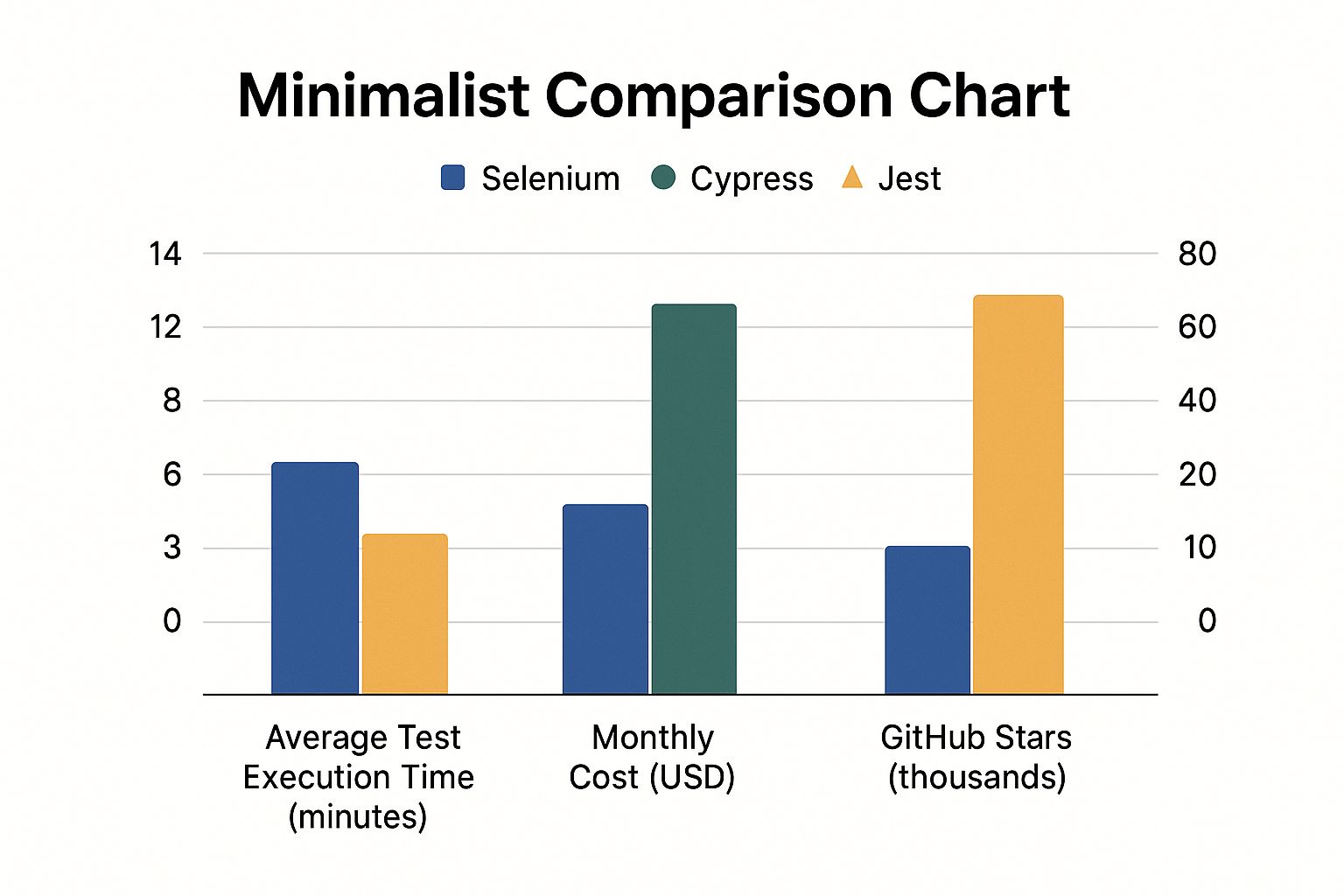
The data highlights the inherent trade-offs. Open-source titans like Selenium boast massive community support (indicated by GitHub stars) but often require more initial setup and can have slower test cycles without optimization. Other tools offer a different balance of speed, features, and cost.
Feature Matrix of Leading Automated Testing Tools
For a direct, apples-to-apples comparison, a side-by-side feature breakdown is invaluable. This table dissects what each tool offers across the most critical dimensions of test automation.
| Feature | Selenium | Cypress | Playwright | Katalon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Approach | Code-based, open-source framework | Code-based, all-in-one framework | Code-based, modern framework | Low-code, all-in-one platform |
| Language Support | Java, Python, C#, JavaScript, Ruby, etc. | JavaScript / TypeScript only | JavaScript / TypeScript, Python, Java, .NET | Groovy / Java (with a keyword-driven manual view) |
| Cross-Browser | Excellent (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, IE) | Good (Chromium-based, Firefox, WebKit), but historically limited | Excellent (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit) | Very good (ships with drivers for major browsers) |
| Execution Speed | Can be slow without parallel execution | Generally fast due to in-browser execution | Very fast due to modern architecture | Moderate; depends on test complexity |
| Debugging | Relies on IDE debuggers; can be complex | Excellent; features a time-traveling GUI | Very good; includes tracing and debugging tools | Good; provides screenshots and logs for failed steps |
| Setup & Maintenance | High; you build and maintain the entire framework | Low; comes with everything you need out-of-the-box | Low; easy to install and get started | Very low; it’s a packaged solution |
| Best For | Large enterprises needing flexibility and wide browser coverage. | Development teams focused on modern web apps and a great developer experience. | Teams wanting fast, reliable tests across all major browsers with modern features. | Teams with mixed skill levels (including manual QAs) needing an all-in-one solution. |
As the table shows, there is no single “best” tool. The optimal choice is entirely dependent on your team’s specific needs and existing skill set.
Selenium: The Established Standard
No discussion of web automation is complete without Selenium. As the original open-source framework, it has been the bedrock of web testing for over a decade. It supports a vast array of programming languages, including Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript. Its primary appeal has always been its unmatched flexibility and cross-browser support.
The trade-off? Selenium’s architecture uses the WebDriver protocol, which communicates with the browser via an intermediary. This can sometimes lead to slower execution and flaky tests compared to newer tools with more direct browser interaction.
- Test Creation: A pure coding experience, ideal for teams with strong programming skills who want complete control to build a custom framework.
- Execution Speed: Can be sluggish out-of-the-box but can achieve high performance for large suites when scaled with a parallel execution solution like Selenium Grid.
- Use Case: Best suited for large enterprises with diverse tech stacks and dedicated automation engineers who require testing across a wide matrix of browsers and operating systems.
Selenium’s greatest strength is also its biggest challenge. It gives you complete freedom, but that also means your team is on the hook for building and maintaining everything else—reporting, assertions, integrations, you name it.
Cypress: A Developer-Focused Experience
Cypress entered the scene with a completely different architectural approach. It runs inside the browser, in the same run loop as your application. This clever design eliminates many of the network-related issues common with Selenium, resulting in faster, more reliable tests.
Cypress is laser-focused on creating an exceptional developer experience. It includes a powerful GUI that shows commands as they execute, with application snapshots for each step, making debugging incredibly intuitive.
- Test Creation: Code-based, using JavaScript, with a clean and powerful API that simplifies common testing tasks.
- Execution Speed: Generally much faster than Selenium for typical scenarios due to its in-browser execution model.
- Debugging: This is Cypress’s standout feature. The time-traveling capability in its Test Runner GUI is a game-changer, allowing you to see exactly what the application looked like at any point during the test.
However, Cypress is not without limitations. It exclusively supports JavaScript/TypeScript and historically had limited cross-browser support (though it has since added Firefox and WebKit support). It also operates within a single browser tab, making scenarios involving multiple tabs or windows difficult to test.
Playwright: Microsoft’s Modern Contender
Developed by Microsoft, Playwright is a newer framework that has rapidly gained popularity. Like Cypress, it aims to solve the flakiness of older tools, but with a different architecture. Playwright uses the WebSocket protocol for browser communication, enabling extremely fast and reliable automation.
Its killer feature is its outstanding cross-browser and cross-platform support, covering Chromium (Chrome, Edge), WebKit (Safari), and Firefox from day one. It also effortlessly handles tests that span multiple tabs or browser windows—a significant advantage over Cypress.
- Test Creation: A code-first tool with official support for JavaScript/TypeScript, Python, Java, and .NET.
- Key Differentiator: Playwright’s auto-waiting mechanism is a major innovation. It automatically waits for elements to be actionable before interacting with them, eliminating a massive source of flaky tests caused by timing issues.
- Use Case: An excellent choice for modern web applications that require rock-solid testing across all major browsers. With features like network interception and device emulation, it’s a powerhouse for any team comfortable with coding.
Katalon: The All-in-One Solution
Katalon targets a different audience entirely. It is a low-code, comprehensive platform designed to make automation accessible to teams with mixed technical skills. It bundles everything you need—a test recorder, an object spy, built-in reporting, and execution engines—into a single package.
Unlike the other tools on this list, Katalon supports web, API, mobile, and even desktop testing from a unified interface. This makes it an attractive option for teams needing to test across a diverse technology landscape without the complexity of integrating multiple tools.
- Test Creation: It offers a dual-scripting interface. Beginners can use the “Manual View” to create tests with simple keywords, while experts can switch to the “Script View” for custom coding in Groovy or Java.
- Ecosystem: Katalon is a full platform, including Katalon Studio (for test creation), Katalon TestOps (for test orchestration and analytics), and Katalon TestCloud (for cloud-based execution).
- Use Case: Ideal for teams seeking a “batteries-included” solution with a gentle learning curve. It is particularly valuable for QA departments with manual testers transitioning to automation.
Ultimately, tool selection is a strategic decision. A team of JavaScript developers building a single-page app will likely gravitate toward Cypress or Playwright. An enterprise with a complex legacy system and a mixed-skill QA team might find Katalon’s all-in-one model a better fit. Meanwhile, Selenium remains a workhorse for organizations that prioritize flexibility and comprehensive browser coverage, provided they have the engineering resources to manage it. Any meaningful automated testing tools comparison requires weighing these practical trade-offs against your team’s specific context.
Future-Proofing Your Test Automation Strategy
Selecting a tool from an automated testing tools comparison is not just about meeting today’s needs. It’s an investment in a solution that must adapt to the rapid evolution of the software testing industry, driven by advancements in AI and the universal shift to DevOps. Choosing a tool that isn’t designed for these trends is like buying a new phone without 5G—it works now, but its limitations will quickly become a major liability.
The most significant change is the integration of artificial intelligence into testing frameworks. This isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a practical solution to the biggest challenge in test automation: maintenance. For years, teams have been crippled by brittle tests that break with minor UI changes, consuming vast amounts of engineering time.
The Rise of AI in Testing
AI is directly addressing this maintenance burden by creating smarter, more resilient tests. The goal is to dramatically reduce the time spent fixing broken tests, allowing teams to focus on expanding valuable test coverage.
Key AI-driven features to look for include:
- Self-Healing Tests: This is a game-changing capability. When a UI element’s locator (like its ID or XPath) changes, AI algorithms can identify the new locator and automatically update the test script. This feature alone can reclaim a significant portion of the time previously lost to manual test repair.
- AI-Powered Test Generation: Emerging tools can analyze your application to suggest or even generate complete test cases from scratch. This accelerates the creation of a baseline test suite and can uncover edge cases your team might have overlooked.
- Visual AI Testing: Going beyond code-level locators, visual AI validates that the UI looks correct to a human user. It catches visual regressions, layout issues, and subtle inconsistencies that traditional functional tests are completely blind to.
The real power of AI is that it moves the conversation from writing scripts to validating behavior. By handling the tedious mechanics of creating and maintaining tests, AI frees up engineers to think about the quality of the user experience itself.
The Unbreakable Link Between Testing and DevOps
The other dominant trend is the deep fusion of test automation with DevOps. In a modern CI/CD pipeline, testing is not a distinct phase but a continuous, automated process running parallel to development. Fast, reliable automated tests are the lifeblood of this process; without them, the concept of continuous delivery fails.
This tight integration is reshaping the tools we use. One study found that 54% of developers now use DevOps practices to ship code faster. Concurrently, AI’s role in testing is projected to grow at a massive compound annual growth rate of 37.3%. These forces, along with the rise of IoT, demand specialized, deeply integrated testing solutions. You can explore more data with these test management software statistics .
This means your chosen tool must be a first-class citizen in your DevOps ecosystem. It needs a robust command-line interface (CLI), seamless integration with CI servers like Jenkins or GitHub Actions, and support for parallel execution to maintain fast feedback loops. The future of testing is fast, intelligent, and deeply embedded in the development lifecycle. A tool built for this reality won’t just help you keep pace—it will provide a decisive competitive edge.
Finding Your Perfect Automation Tool
Selecting the right tool from our automated testing tools comparison is not a simple checklist exercise. It’s a critical decision that will shape your team’s workflow, budget, and product quality for years. Think of it less as a purchase and more as a long-term partnership. The right tool empowers your team to innovate faster and build better software; the wrong one becomes a persistent source of friction and wasted effort.
The key is to look beyond marketing hype and conduct an honest self-assessment. A tool that’s perfect for a nimble startup could be a disaster for a large, regulated enterprise. The best choice always aligns with your team’s skills, your project’s technology stack, and your company’s strategic goals.
Matching Tools to How Your Team Actually Works
Let’s translate this into practical, real-world scenarios. This is where you connect a tool’s design philosophy to your team’s day-to-day reality.
Here are a few common situations and my recommendations:
-
You’re a Startup with a Small QA Team: Speed and simplicity are paramount. You need to get tests running immediately. In this scenario, a low-code platform like Katalon is an excellent choice. It empowers manual testers or developers to create robust tests for web, API, and mobile platforms without getting bogged down in complex coding.
-
You’re an Enterprise with Complicated Legacy Apps: Your environment includes complex business workflows and older technologies. You need a powerful, stable, and highly flexible solution. A model-based tool like Tricentis Tosca or a custom framework built on Selenium is often the best approach. These tools are designed to handle the kind of intricate business logic and diverse tech stacks that newer, web-first tools may struggle with.
-
You’re a Modern Dev Team Living in JavaScript: If your team builds with frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue, choose a tool that operates in their native environment. Tools like Cypress or Playwright are your best bets. Cypress offers an unparalleled developer experience for writing and debugging tests, while Playwright excels with its raw speed and superior cross-browser capabilities. Both integrate seamlessly into a JavaScript-centric CI/CD pipeline.
The biggest mistake I see teams make is choosing a tool because it’s popular, not because it fits. Playwright is an amazing framework, but if your team is mostly manual testers, it’s going to sit on a shelf collecting digital dust. Always, always pick the tool your team will actually use.
Your Final Gut-Check Before Committing
You’ve narrowed it down to one or two contenders. Before you commit, run your top choices through this final checklist. Answering these questions honestly will prevent significant pain down the road.
- Team Skills: Does this tool align with our team’s technical comfort zone and skill set?
- Tech Coverage: Can it comprehensively test our entire application—web, mobile, and APIs?
- Pipeline Fit: How easily will this integrate into our CI/CD pipeline? Will it require extensive custom work?
- Maintenance Burden: Realistically, how much time will we spend fixing broken tests versus writing new ones?
- True Cost: What is the total cost of ownership? Consider licensing, training, setup, and ongoing support costs.
Choosing your automation tool is where strategy meets execution. By focusing on these practical considerations, you can select a solution that doesn’t just look good on paper but delivers a tangible return on your investment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Automation Tools
When you’re comparing automated testing tools, a lot of the same questions tend to pop up. Thinking through the practical side of things—cost, setup, and what the tool can actually do—is key to picking the right one for your team.
What’s the Real Difference Between Open-Source and Commercial Tools?
This is the classic debate, and it really comes down to a trade-off between freedom and convenience.
Open-source options like Selenium or Playwright are completely free, which is a huge plus. They’re also incredibly flexible and backed by massive communities. The catch? That freedom means you need some serious technical chops to build and maintain a full testing framework from scratch.
On the other hand, commercial tools like Katalon or Leapwork are designed to be all-in-one platforms. They often give you low-code or no-code interfaces, dedicated support, and slick reporting dashboards right out of the box, but you’ll be paying for those licenses. The right choice depends on your budget, your team’s existing skills, and whether you prefer vendor support over community forums.
How Do I Actually Plug a Testing Tool into My CI/CD Pipeline?
Most modern testing tools are built with CI/CD in mind. The setup usually involves telling your CI server—whether it’s Jenkins , GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions—how to run your tests automatically. This is almost always handled through the tool’s command-line interface (CLI).
You’ll typically add a step to your pipeline that installs the tool and its dependencies. Then, you execute a command to kick off the tests. The tool feeds the results back to the server, which then decides if the build passes or fails, giving your developers instant feedback.
Can I Find One Tool for Web, Mobile, and API Testing?
You can, but it’s a matter of choosing between a jack-of-all-trades or a team of specialists.
Many modern platforms, like Katalon Studio , are built to handle web, API, mobile, and even desktop tests from a single interface. This is a great way to simplify your toolchain and get everyone on the same page.
The alternative is to build a “best-of-breed” stack by combining specialized tools. For example:
- Web Testing: Using a powerhouse like Playwright or Selenium.
- API Testing: Relying on a dedicated tool like Postman or REST Assured.
- Mobile Testing: Turning to the industry standard, Appium, for native apps.
This approach gives you maximum control and power in each area, but it takes more work to integrate and manage everything. It all depends on whether your team values a single, unified platform or the focused capabilities of individual tools.
Ready to stop hallucinating and start building? Context Engineering connects to your IDE to give AI agents the precise project context they need, transforming complex feature development into a streamlined, automated workflow. Drastically reduce trial-and-error and build reliable software faster.